- Written by Shafiul Azam
- Category: গবেষণা ফিচার
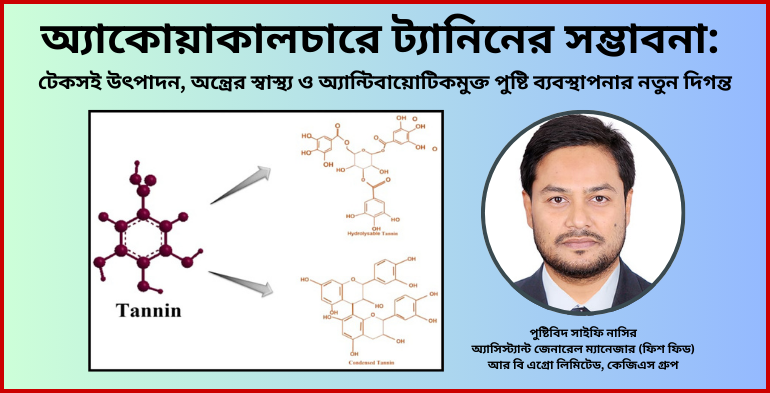
এগ্রিলাইফ প্রতিবেদক:অ্যাকোয়া নিউট্রিশন ও অ্যাকোয়াকালচার শিল্পে ট্যানিন (Tannin) বর্তমানে একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ প্রাকৃতিক বায়োঅ্যাকটিভ যৌগ হিসেবে নতুন সম্ভাবনার দ্বার উন্মোচন করছে। পুষ্টিবিদ সাইফি নাসিরের বিশ্লেষণ অনুযায়ী, ট্যানিন হলো এক ধরনের প্রাকৃতিক পলিফেনলিক যৌগ, যা উদ্ভিদের বাকল, পাতা, বীজ, ফল ও কান্ডে পাওয়া যায় এবং মাছ ও চিংড়ির খাদ্যে একটি কার্যকর, নিরাপদ ও অ্যান্টিবায়োটিকমুক্ত সংযোজন হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হচ্ছে। ট্যানিনকে অনেক সময় ট্যানিক অ্যাসিডও বলা হয়, যা সাধারণত চেস্টনাট, কোয়ার্কাস, সিসালপিনিয়া ও অন্যান্য উদ্ভিদ উৎস থেকে সংগ্রহ করা হয়। আধুনিক অ্যাকোয়াফিড শিল্পে যখন ফিশমিলের বিকল্প হিসেবে উদ্ভিদভিত্তিক প্রোটিনের ব্যবহার বাড়ছে, তখন সেইসব উপাদানে উপস্থিত পলিফেনলিক ট্যানিন পুষ্টি ব্যবস্থাপনায় গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকা রাখছে।
- Written by Shafiul Azam
- Category: গবেষণা ফিচার

ড. মোহাম্মদ খালেকুজ্জামান,মহাপরিচালক, বাংলাদেশ ধান গবেষণা ইনস্টিটিউট (ব্রি)
পরিবর্তিত বাস্তবতায় বাংলাদেশের কৃষি
বাংলাদেশের কৃষি আজ এক জটিল বাস্তবতার মুখোমুখি। জনসংখ্যা এখনো বছরে প্রায় ১.১২ শতাংশ হারে বাড়ছে, কিন্তু আবাদি জমি কমছে প্রায় ০.২৪ শতাংশ হারে। স্বাধীনতার সময় মাথাপিছু জমির পরিমাণ ছিল ২৮ শতক; এখন তা ১০ শতকের নিচে নেমে গেছে। এর সঙ্গে যুক্ত হয়েছে জমির উর্বরতা কমে যাওয়া, নগরায়ণ, শিল্পায়ন আর জলবায়ু পরিবর্তনের নানা প্রভাব।
- Written by Shafiul Azam
- Category: গবেষণা ফিচার

এগ্রিলাইফ২৪ ডটকমঃদক্ষিণ এশিয়ায় জলবায়ু পরিবর্তনের প্রেক্ষাপটে টেকসই কৃষি ব্যবস্থার সম্ভাবনা তুলে ধরে “Potentials of Agroforestry for Rural Development and Climate Resilient Farming in South Asia” শীর্ষক একটি নতুন গবেষণাগ্রন্থ প্রকাশ করেছে সার্ক সার্ক কৃষি কেন্দ্র। গতকাল সোমবার (৯ মার্চ ২০২৬) ঢাকার অমর একুশে বইমেলায় আয়োজিত এক অনুষ্ঠানে বইটির মোড়ক উন্মোচন করা হয়। বইটি সম্পাদনা করেছেন ড. রাজা উল্লাহ খান, ড. মো. হারুনুর রশিদ, পলাশ চন্দ্র গোস্বামী এবং মো. আবুল বাশার। এতে দক্ষিণ এশিয়ায় গ্রামীণ জীবিকা উন্নয়ন ও জলবায়ু সহনশীল কৃষি ব্যবস্থায় আগ্রোফরেস্ট্রির গুরুত্ব তুলে ধরা হয়েছে।
- Written by Shafiul Azam
- Category: গবেষণা ফিচার

বাকৃবি প্রতিনিধি:দীর্ঘ গবেষণার পর দেশে আমন ধানের নতুন দুটি জাত উদ্ভাবন করেছে বাংলাদেশ পরমাণু কৃষি গবেষণা ইনস্টিটিউট (বিনা)। উচ্চফলন, ব্লাস্ট রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা ও উন্নত পুষ্টিগুণের সমন্বয়ে উদ্ভাবিত হয়েছে ‘বিনা ধান২৭’ ও ‘বিনা ধান২৮’ নামের এই দুটি জাত। সম্প্রতি কৃষি মন্ত্রণালয়ে অনুষ্ঠিত জাতীয় বীজ বোর্ডের ১১৫তম সভায় জাত দুটি সারাদেশে চাষাবাদের জন্য আনুষ্ঠানিকভাবে অনুমোদন পেয়েছে। এর মাধ্যমে বিনার উদ্ভাবিত ধানের মোট জাতের সংখ্যা দাঁড়াল ২৮-এ। বিনার উদ্ভিদ প্রজনন বিভাগের গবেষকদল এই দু’টি ধানের জাত উদ্ভাবন করেন।
অ্যান্টিমাইক্রোবিয়াল রেজিস্ট্যান্স ও ভারী ধাতুর প্রভাব মোকাবিলায় ‘ওয়ান হেলথ’ মডেলে বাকৃবির গবেষণা
- Written by Shafiul Azam
- Category: গবেষণা ফিচার

বাকৃবি প্রতিনিধি:বিশ্বজুড়ে জনস্বাস্থ্যের জন্য অন্যতম বড় হুমকি হয়ে দাঁড়িয়েছে অ্যান্টিমাইক্রোবিয়াল রেজিস্ট্যান্স (এএমআর) বা জীবাণুর ওষুধ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা। এর সঙ্গে যুক্ত হয়েছে জলবায়ু পরিবর্তনের নেতিবাচক প্রভাব, যা পশুপালন ও খাদ্য নিরাপত্তাকে ঠেলে দিচ্ছে চরম ঝুঁকির মুখে। এই জটিল ও আন্তঃসম্পর্কিত চ্যালেঞ্জ মোকাবিলায় ‘ক্লাইমেট-স্মার্ট’ বা জলবায়ু-সহিষ্ণু কৌশল উদ্ভাবনে নতুন একটি গবেষণা প্রকল্প শুরু করেছে বাংলাদেশ কৃষি বিশ্ববিদ্যালয় (বাকৃবি)।
- Written by Shafiul Azam
- Category: গবেষণা ফিচার

সিকৃবি প্রতিনিধি: সিলেট কৃষি বিশ্ববিদ্যালয় রিসার্চ সিস্টেমের (সাউরেস) তত্ত্বাবধানে বিশ্ববিদ্যালয় মঞ্জুরী কমিশনের অর্থায়নে দুই দিন ব্যাপী ২০২৫-২৬ অর্থ বছরের গবেষনা প্রকল্প বিশেষজ্ঞ মুল্যায়নকারী দ্বারা মূল্যায়ন করে আজ ৪ মার্চ (বুধবার) ভাইস-চ্যান্সেলর প্রফেসর ড. মোঃ আলিমুল ইসলাম এর সভাপতিত্বে প্রফেসর ড. ইকবাল হোসেন কনফারেন্স রুমে ২২তম রিসার্চ এডভাইজারি কমিটির সভা অনুষ্ঠিত হয়।
























